Page 43 - DIAGEN-EN
P. 43
primeFISH Products
MICRODELETION Mikrodeletion Panel
PANEL
17-018-A PW/ANGELMAN
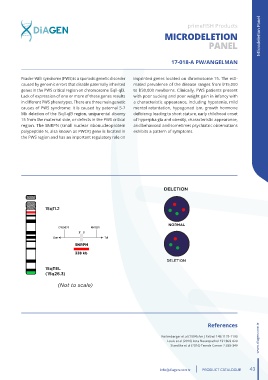
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a sporadic genetic disorder imprinted genes located on chromosome 15. The esti-
caused by genomic errors that disable paternally inherited mated prevalence of the disease ranges from l/15,000
genes in the PWS critical region on chromosome l5qll-ql3. to l/30,000 newborns. Clinically, PWS patients present
Lack of expression of one or more of these genes results with poor sucking and poor weight gain in infancy with
in different PWS phenotypes. There are three main genetic a characteristic appearance, including hypotonia, mild
causes of PWS syndrome: it is caused by paternal 5-7 mentol retardation, hypogonad ism, growth hormone
Mb deletion of the l5qll-ql3 region, uniparental disomy deficiency leading to short stature, early childhood onset
15 from the maternal side, or defects in the PWS critical of hyperpha gia and obesity, characteristic appearance,
region. The SNRPN (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein and behavioral and sometimes psychiatric observations
polypeptide N, alsa known as PWCR) gene is located in exhibits a pattern of symptoms.
the PWS region and has an important regulatory role on
MICRODELETION
15q11.2 D15S677 RH1251
3' 5'
NORMAL
Cent Tel
SNRPN
338 kb
DELETION
15qTEL (15q26.3)
(Not to scale)
References
Reifenberger et al (1994) Am J Pathol 145:1175-1190 www.diagen.com.tr
Louis et al (2016) Acta Neuropathol 131:803-820
Staedtke et al (2016) Trends Cancer 2:338-349
PRODUCT CATALOGUE 43